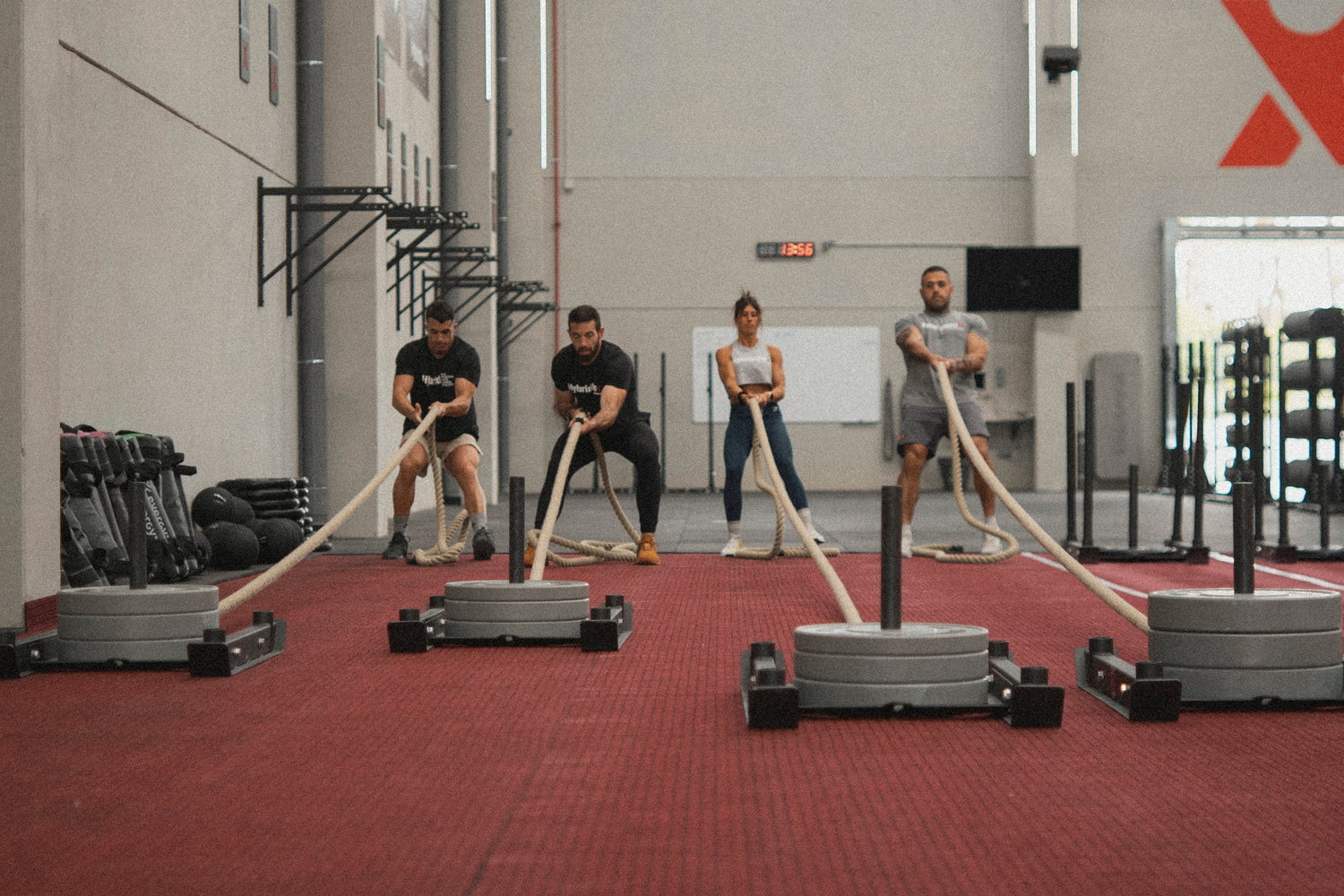
Hybrid training combines different types of exercises to develop multiple physical abilities in an integral way. It is based on movements of low technical complexity, which allows it to easily adapt to any level. These exercises can be carried out at intervals or continuously, and its main objective is Improve performance In various sports disciplines or simply contribute to better general health.

What is hybrid training?
Hybrid training mixes sessions focused on force development (such as basic surveys) with cardiovascular resistance work (race, rowing, bike), achieving a complete physical development without neglecting any quality. It differs from Cross-Training in which it is more structured, with a planned progression and a controlled intensity.
Differences with other methodologies:
In recent years, the world of functional training has grown very strongly and has generated several branches among them two stand out: hybrid training and Cross-Training. Although they share many things in common between intensity, functionality and health. The two are training methodologies with a common approach, improving people's fitness.
| Aspect | Hybrid training | Cross Training |
|---|---|---|
| Technical complexity | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Work zone (FC) | Zones 2-3 (moderate heart rate) | Zones 3-4 (higher heart rate) |
| Format | Fixed Stations + Carrera | Variable training (Wods, Emoms, Amraps, etc.) |
| Structure | More predictable, with constant rhythm | More varied, with frequent changes of rhythm and intensity |
| Main objective | Resistance + Simple Functional Strength | Power, technique and multidisciplinary performance |

What is a hybrid athlete?
A hybrid athlete is a person who trains all fundamental physical abilities, especially strength and resistance, with the aim of rendering both in specific sports and hybrid competitions. This type of training combines weightlifting, functional exercises and cardiovascular work, achieving a complete and adaptable physical preparation.
Since the approach usually has a greater load of aerobic and metabolic resistance, hybrid training can be carried out with a high frequency, even daily, always taking into account the adaptation, experience and individual recovery of each person.
Types of training sessions:
| Mode | Description | Main benefit |
|---|---|---|
| EMOM | Every minute a series of exercises are performed and what remains of time is rest. | Improves interval resistance and rhythm management. |
| Couple work or equipment | Synchronized training or with repetitions to be distributed among members. | It encourages communication, teamwork and competitiveness. |
| Series | Series with fixed repetitions and predetermined breaks (long or short). | Improves resistance capacity and recovery. |
| For time | Complete a set of exercises in the shortest possible time. | It enhances resistance, efficiency and strategy. |
| Skills | Specific technical work to improve efficiency in a specific movement. | Perfect the technique and optimize the performance in key exercises. |

Benefits of hybrid training:
1. Full physical development: It combines strength, resistance, mobility and control.
2. Better adhesion to the plan: Being varied and progressive, avoid monotony.
3. Reduction of injury risk: Not focusing only on a quality, there is less specific overload.
4. Time efficiency: You train more in less time.
5. Controlled interference: Being well planned, there are no conflicts between strength and cardio development.
Possible disadvantages (and how to avoid them)
- Accumulated fatigue: If it is not planned properly, it can generate overcoming.
- Need for precise programming: It is key to alternate well strength and cardio, and respect recovery.
Tips to start in hybrid training:
- Start with an aerobic base: 4-6 weeks of low intensity cardio.
- Do not neglect the technique: prioritize the right gesture before increasing loads or speed.
- Control the weekly volume: less is more if you are a beginner.
- Listen to your body and adjust the plan to your lifestyle.
Basic equipment for hybrid training and competition:
| Element | Main use |
|---|---|
| Thrust and drag sled (sled) | Improves the force of legs, traction and cardiovascular capacity. |
| Box / drawer plyo | Saltos, Step overs, plyometric work. |
| Kettlebells / dumbbells | Displacements, snatches, carries, swings. |
| Sandbags | Surveys, unstable charges, transport. |
| Medball | Shots to the wall, launches, postural control. |
| Traction strings | Drag simulations, pull power tests. |
| Running or Air Runner tapes | Controlled career work. |
| Concept2 Row / Skierg / Bikeerg | Cardiovascular resistance work in stations. |
| Light discs and bars | Basic surveys without high technical complexity. |
All these materials allow simulating the environment of a hybrid competition and adapting training in both boxes and outdoors.
Conclusion:
Hybrid training is a versatile, efficient and effective methodology that allows you to develop strength and resistance without compromising the results. With well structured programming, you can improve your general performance, reduce the risk of injuries and enjoy a challenging and varied routine.
This approach is ideal whether you are starting in the world of fitness, as if you are an amateur athlete who seeks to enhance its performance or simply want to be part of an active community oriented to integral well -being.